Rabbit IFN gamma Polyclonal Antibody - Biotinylated
Interferon-gamma (IFN-gamma) is a dimerized soluble cytokine that is the only member of the type II class of interferons. This interferon was originally called macrophage-activating factor, a term now used to describe a larger family of proteins to which IFN-gamma belongs. IFN-gamma, or type II interferon, is a cytokine that is critical for innate and adaptive immunity against viral and intracellular bacterial infections and for tumor control. Aberrant IFN-gamma expression is associated with a number of autoinflammatory and autoimmune diseases. The importance of IFN-gamma in the immune system stems in part from its ability to inhibit viral replication directly, but, most important, derives from its immunostimulatory and immunomodulatory effects. IFN-gamma is produced predominantly by natural killer (NK) and natural killer T (NKT) cells as part of the innate immune response, and by CD4 and CD8 cytotoxic T lymphocyte (CTL) effector T cells once antigen-specific immunity develops.
Reactivity - ELISA
Bovine IFN gamma - None
Canine IFN gamma - None
Caprine IFN gamma - None
Chicken IFN gamma - None
Dolphin IFN gamma - Weak
Equine IFN gamma - None
Feline IFN gamma - None
Ferret IFN gamma - None
Human IFN gamma - Weak
Mouse IFN gamma - None
Ovine IFN gamma - None
Rabbit IFN gamma - Strong
Swine IFN gamma - None
Zebrafish IFN gamma 1-1 - None
Zebrafish IFN gamma 1-2 - None
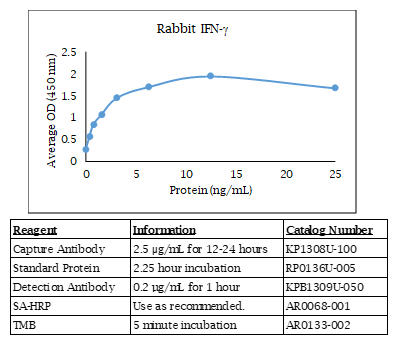
Rabbit IFN gamma ELISA Data
Evaluation of a DNA Aβ42 Vaccine in Aged NZW Rabbits: Antibody Kinetics and Immune Profile after Intradermal Immunization with Full-Length DNA Aβ42 Trimer.
Lambracht-Washington D, Fu M, Wight-Carter M, Riegel M, Rosenberg RN.
J Alzheimers Dis. 2017;57(1):97-112. doi: 10.3233/JAD-160947.
Applications: Determine frequencies of cytokine secreting cells by ELISPOT for rabbit IFN gamma, IL-17A, and IL-4.
Ordering Information & Terms and Conditions
We require a phone number and e-mail address for both the end user of the ordered product and your institution's Accounts Payable representative. This information is only used to help with technical and billing issues.
Via Phone
Please call us at 651-646-0089 between the hours of 8:30 a.m. and 5:30 p.m. CST Mon - Fri.
Via Fax
Orders can be faxed to us 24 hours a day at 651-646-0095.
Via E-mail
Please e-mail orders to orders@KingfisherBiotech.com.
Via Mail
Please mail your order to:
Sales Order Entry
Kingfisher Biotech, Inc.
1000 Westgate Drive
Suite 123
Saint Paul, MN 55114
USA
Product Warranty
Kingfisher Biotech brand products are warranted by Kingfisher Biotech, Inc. to meet stated product specifications and to conform to label descriptions when used, handled and stored according to instructions. Unless otherwise stated, this warranty is limited to one year from date of sale. Kingfisher Biotech’s sole liability for the product is limited to replacement of the product or refund of the purchase price. Kingfisher Biotech brand products are supplied for research applications. They are not intended for medicinal, diagnostic or therapeutic use. The products may not be resold, modified for resale or used to manufacture commercial products without prior written approval from Kingfisher Biotech.
Payment Terms
All prices are subject to change without notice. Payment terms are net thirty (30) days from receipt of invoice. A 1.5% service charge per month is added for accounts past due over 30 days. Prices quoted are U.S. Dollars. The purchaser assumes responsibility for any applicable tax. You will only be charged for products shipped. Products placed on back order will be charged when shipped. If you place an order and fail to fulfill the terms of payment, Kingfisher Biotech, Inc. may without prejudice to any other lawful remedy defer further shipments and/or cancel any order. You shall be liable to Kingfisher Biotech, Inc. for all costs and fees, including attorneys' fees, which Kingfisher Biotech, Inc. may reasonably incur in any actions to collect on your overdue account. Kingfisher Biotech, Inc. does not agree to, and is not bound by, any other terms or conditions such as terms in a purchase order that have not been expressly agreed to in writing signed by a duly authorized officer of Kingfisher Biotech, Inc.
Shipping
Shipping and handling costs are prepaid and added to the invoice. Shipping and handling costs will be charged only on the first shipment in situations where an order contains back ordered products. Kingfisher Biotech, Inc. reserves the right to select the packaging and shipping method for your order, which will ensure the stability of the product and also efficient tracing. Domestic orders will normally be shipped by overnight. Damage during shipment is covered by the warranty provided in these terms and conditions. For international orders, title to the goods passes in the United States when the goods are placed with the shipper. For all orders, the risk of loss of the goods passes when the goods are placed with the shipper.
Returns
Please call customer service before returning any products for refund, credit or replacement. NO returns will be accepted without prior written authorization. Returns are subject to a restocking fee of 20%.



 New Products
New Products Ordering
Ordering Distributors
Distributors Resources
Resources FAQs
FAQs Cart
Cart