Bovine IL-8 (CXCL8) Polyclonal Antibody
Interleukin-8 (IL-8), also known as CXCL8, is a CXC family member chemokine produced by macrophages and other cell types such as epithelial cells. There have been 17 different CXC chemokines described in mammals, that are subdivided into two categories, those with a specific amino acid sequence (or motif) of glutamic acid-leucine-arginine (or ELR for short) immediately before the first cysteine of the CXC motif (ELR-positive), and those without an ELR motif (ELR-negative). ELR-positive CXC chemokines such as IL-8 specifically induce the migration of neutrophils, and interact with chemokine receptors CXCR1 and CXCR2.
Reactivity - ELISA
Bovine IL-8 - Strong
Canine IL-8 - Moderate
Dolphin IL-8 - Moderate
Equine IL-8 - Weak
Feline IL-8 - None
Guinea Pig IL-8 - None
Human IL-8 - None
Rabbit IL-8 - Weak
Swine IL-8 - Weak
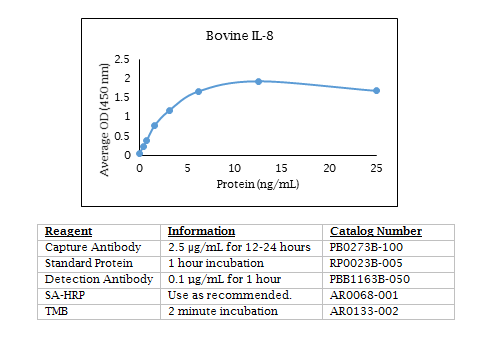
Bovine IL-8 ELISA Data
Host Factors Determine the Evolution of Infection With Staphylococcus Aureus to Gangrenous Mastitis in Goats.
Rainard P, Gitton C, Chaumeil T, Fassier T, Huau C, Riou M, Tosser-Klopp G, Krupova Z, Chaize A, Gilbert FB, Rupp R, Martin P.
Vet Res. 2018 Jul 25;49(1):72. doi: 10.1186/s13567-018-0564-4.
Applications: Measurement of goat IL-8 in milk by ELISA
Abstract
Staphylococcus aureus is the major cause of very severe mastitis of dairy goats. The initial objective of our study was to fine-tune an experimental model of infection of the goat mammary gland with two strains of S. aureus and two lines of goats (low and high somatic cell score lines). Following the challenge, the 10 infected goats divided in two clear-cut severity groups, independently of the S. aureus strain and the goat line. Five goats developed very severe mastitis (of which four were gangrenous) characterized by uncontrolled infection (UI group), whereas the other five kept the infection under control (CI group). The outcome of the infection was determined by 18 h post-infection (hpi), as heralded by the bacterial milk concentration at 18 hpi: more than 107/mL in the UI group, about 106/mL in the CI group. Leukocyte recruitment and composition did not differ between the groups, but the phagocytic killing at 18 hpi efficiency did. Contributing factors involved milk concentrations of α-toxin and LukMF' leukotoxin, but not early expression of the genes encoding the pentraxin PTX3, the cytokines IL-1α and IL-1β, and the chemokines IL-8 and CCL5. Concentrations of TNF-α, IFN-γ, IL-17A, and IL-22 rose sharply in the milk of UI goats when infection was out of control. The results indicate that defenses mobilized by the mammary gland at an early stage of infection were essential to prevent staphylococci from reaching critical concentrations. Staphylococcal exotoxin production appeared to be a consequent event inducing the evolution to gangrenous mastitis.
Ordering Information & Terms and Conditions
We require a phone number and e-mail address for both the end user of the ordered product and your institution's Accounts Payable representative. This information is only used to help with technical and billing issues.
Via Phone
Please call us at 651-646-0089 between the hours of 8:30 a.m. and 5:30 p.m. CST Mon - Fri.
Via Fax
Orders can be faxed to us 24 hours a day at 651-646-0095.
Via E-mail
Please e-mail orders to orders@KingfisherBiotech.com.
Via Mail
Please mail your order to:
Sales Order Entry
Kingfisher Biotech, Inc.
1000 Westgate Drive
Suite 123
Saint Paul, MN 55114
USA
Product Warranty
Kingfisher Biotech brand products are warranted by Kingfisher Biotech, Inc. to meet stated product specifications and to conform to label descriptions when used, handled and stored according to instructions. Unless otherwise stated, this warranty is limited to one year from date of sale. Kingfisher Biotech’s sole liability for the product is limited to replacement of the product or refund of the purchase price. Kingfisher Biotech brand products are supplied for research applications. They are not intended for medicinal, diagnostic or therapeutic use. The products may not be resold, modified for resale or used to manufacture commercial products without prior written approval from Kingfisher Biotech.
Payment Terms
All prices are subject to change without notice. Payment terms are net thirty (30) days from receipt of invoice. A 1.5% service charge per month is added for accounts past due over 30 days. Prices quoted are U.S. Dollars. The purchaser assumes responsibility for any applicable tax. You will only be charged for products shipped. Products placed on back order will be charged when shipped. If you place an order and fail to fulfill the terms of payment, Kingfisher Biotech, Inc. may without prejudice to any other lawful remedy defer further shipments and/or cancel any order. You shall be liable to Kingfisher Biotech, Inc. for all costs and fees, including attorneys' fees, which Kingfisher Biotech, Inc. may reasonably incur in any actions to collect on your overdue account. Kingfisher Biotech, Inc. does not agree to, and is not bound by, any other terms or conditions such as terms in a purchase order that have not been expressly agreed to in writing signed by a duly authorized officer of Kingfisher Biotech, Inc.
Shipping
Shipping and handling costs are prepaid and added to the invoice. Shipping and handling costs will be charged only on the first shipment in situations where an order contains back ordered products. Kingfisher Biotech, Inc. reserves the right to select the packaging and shipping method for your order, which will ensure the stability of the product and also efficient tracing. Domestic orders will normally be shipped by overnight. Damage during shipment is covered by the warranty provided in these terms and conditions. For international orders, title to the goods passes in the United States when the goods are placed with the shipper. For all orders, the risk of loss of the goods passes when the goods are placed with the shipper.
Returns
Please call customer service before returning any products for refund, credit or replacement. NO returns will be accepted without prior written authorization. Returns are subject to a restocking fee of 20%.



 New Products
New Products Ordering
Ordering Distributors
Distributors Resources
Resources FAQs
FAQs Cart
Cart